Leica M125 C, M205 C, and M205 Microscopes
Encoded Stereo Microscopes
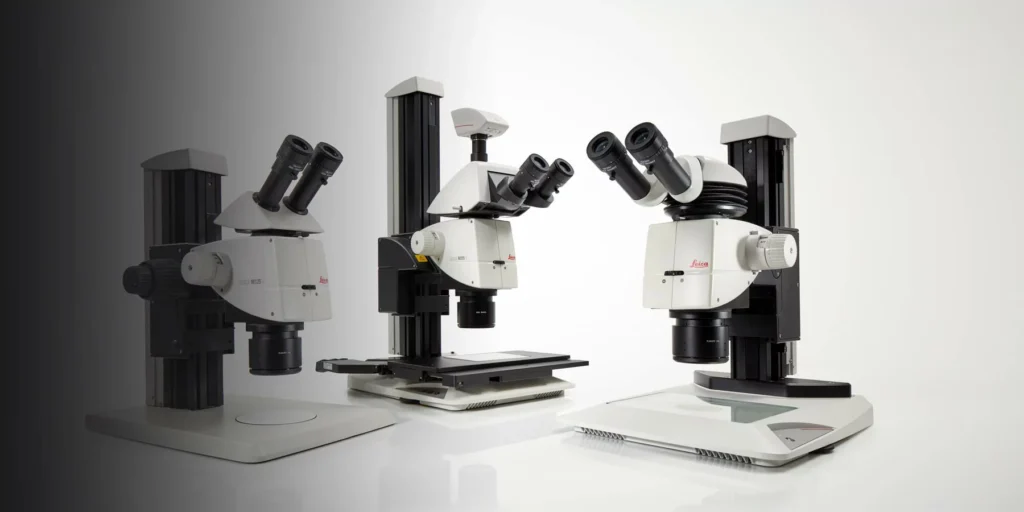

Leica M125 C, M205 C and M205 A encoded stereo microscopes are high‑performance systems designed to deliver reproducible, calibrated 3D images for demanding inspection and research tasks. They combine encoded zoom with apochromatic optics, wide magnification ranges and, on M205 models, FusionOptics technology for both high resolution and large depth of field. The M205 A adds full motorization and automation, making it especially suited to repetitive workflows that require consistent results with minimal manual adjustment.
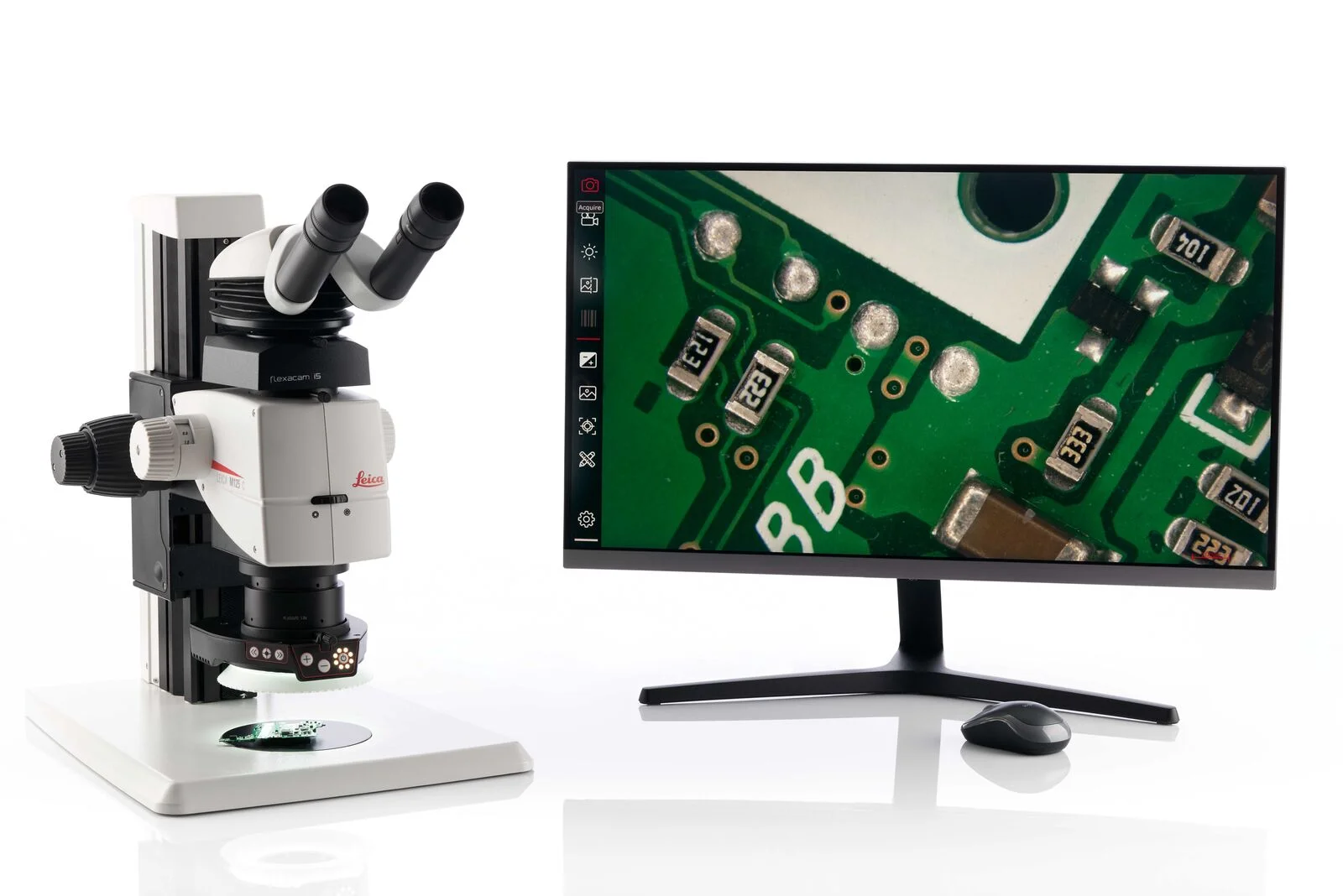

Encoded zoom and apochromatic optics make M125 C a reliable workhorse for routine but critical inspections where clear 3D images and scale‑correct documentation are important.
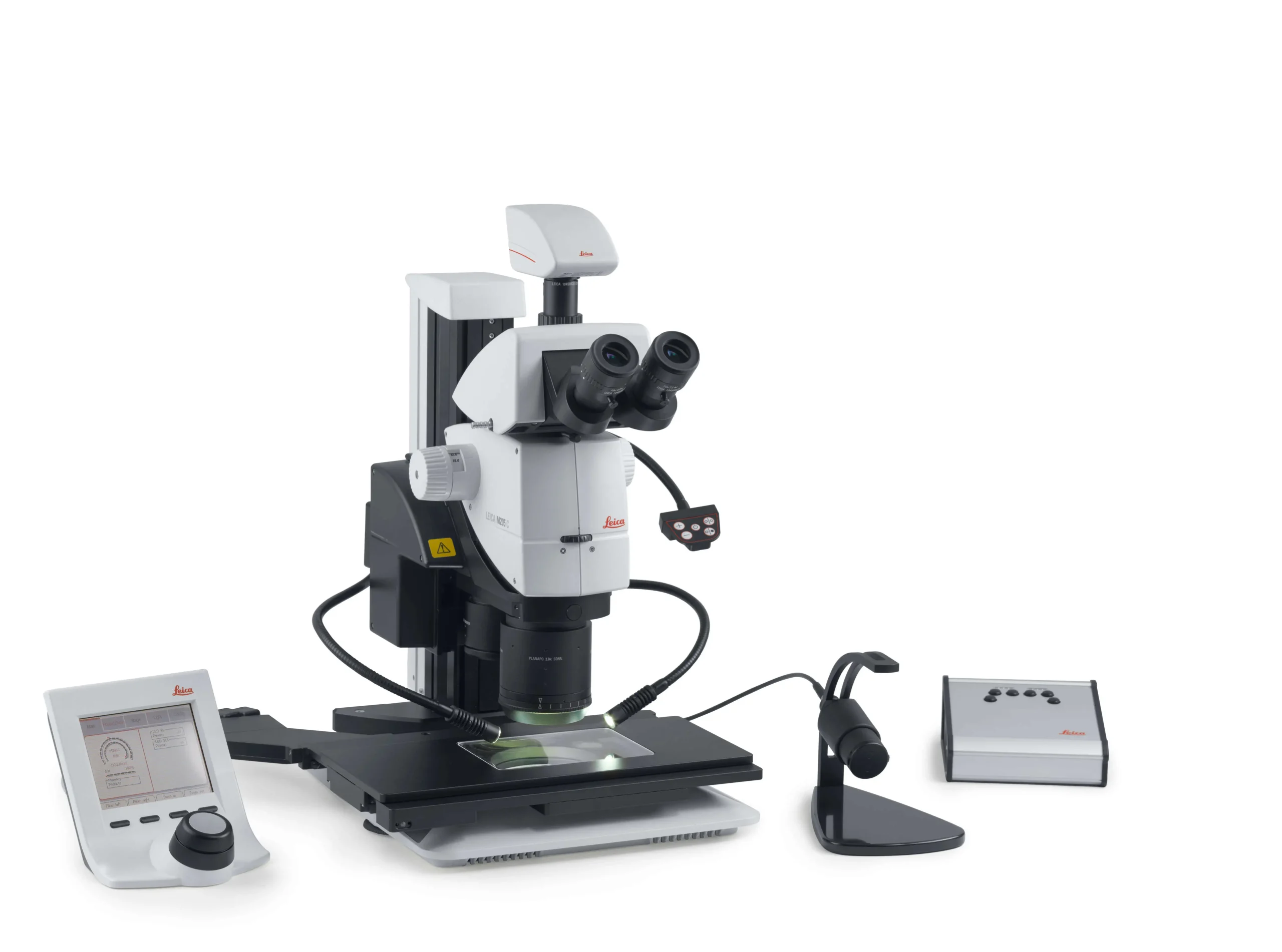
M205 C combines a wide 20.5:1 zoom with FusionOptics to deliver very high resolution and depth of field, ideal for applications where the finest surface details must remain sharply visible.
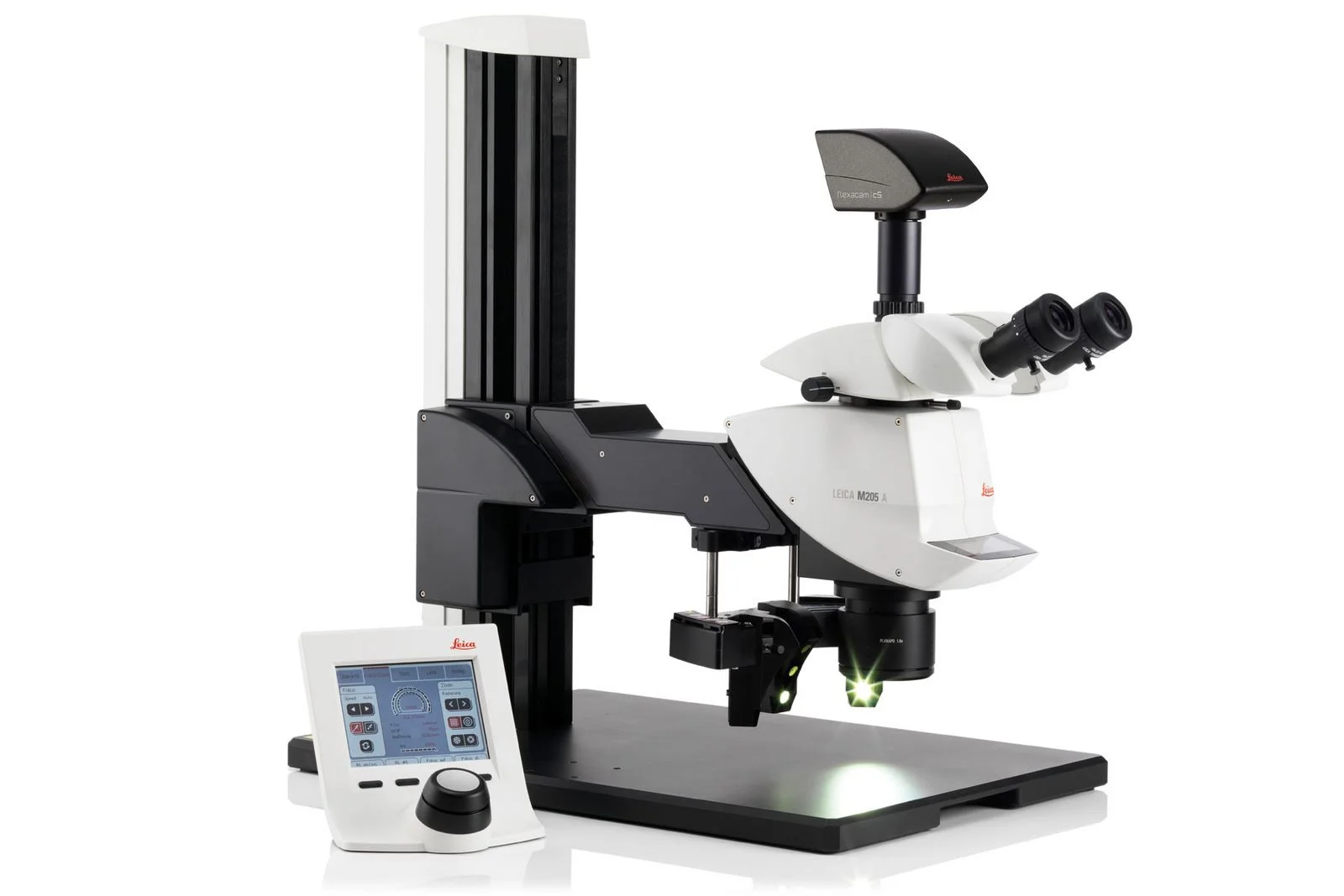

With motorized zoom and focus on the same FusionOptics platform, M205 A supports automated routines and repeatable imaging, helping standardize complex QA or R&D workflows.
Technical Specifications of Encoded Stereo Microscopes
Industries We Serve
M125 C, M205 C & M205 A encoded stereo microscopes support demanding industrial and research applications.
Key Features and Benefits of Encoded Stereo Microscopes
Image coding continuously transmits zoom and iris diaphragm settings to the software, so scale bars and calibration update automatically and key parameters are stored with every image.
- Easily recall settings to capture comparable images across sessions.
- Reduces user‑to‑user variation, supporting consistent documentation.
Advanced apochromatic optics provide high‑contrast, color‑true images with strong 3D impression, revealing fine structures and critical details.
- M125 C offers up to 864 lp/mm resolution with a 2.0× PlanApo objective.
- M205 C/M205 A reach up to 1050 lp/mm and sub‑micrometer visible structure widths.
FusionOptics technology in the M205 range uses one beam path for maximum resolution and the other for maximum depth of field, which the brain merges into a crisp 3D image.
- See tiny details clearly over uneven or structured surfaces.
- Ideal for PCBs, medical devices, and complex material samples.
Large encoded zoom ranges let users switch quickly between overview and high magnification while maintaining parfocal imaging.
- M125 C: 12.5:1 zoom with typical 8×–100× magnification.
- M205 C/M205 A: 20.5:1 zoom with approximately 7.8×–160× magnification.
The fully automated M205 A allows motorized control of zoom, focus, and illumination via SmartTouch or software, simplifying repetitive, high‑precision tasks.
- Run standardized imaging sequences with just a few clicks.
- Increase throughput while maintaining consistent image quality.
A wide range of stands, Ergo accessories, illuminations, and digital cameras lets each microscope be configured for specific industrial or life‑science workflows.
- Ergonomic components support comfortable, precise work over long sessions.
- Different illumination and camera options adapt the system to many sample types.
The M‑series encoded stereo microscopes are used in medical device manufacturing, semiconductor and electronics inspection, and materials science laboratories.
- Support consistent, documented inspection across multiple operators and shifts.
- Help detect defects early with high‑quality, repeatable imaging.
Applications and Usecases of Encoded Stereo Microscopes
Inspect complex medical components, such as implants, catheters, and surgical instruments, to verify manufacturing quality and cleanliness.
- Checking surface finish and edges on metallic and polymer components.
- Evaluating assembly quality of multi‑part devices and moving mechanisms.
- Documenting inspection results with calibrated, repeatable images for regulatory records.
Use the large zoom range and high resolution to analyse wafers, packaged devices, wire bonds, and interconnects.
- Inspecting wire bonds, pads, and fine structures for defects or contamination.
- Examining cross‑sections of solder joints and micro‑features with excellent depth of field.
- Supporting failure analysis and process optimization with detailed stereo images.
Characterize structure, defects, and failure modes in metals, polymers, composites, and other engineering materials.
- Analysing fractures, cracks, and wear patterns on components and test specimens.
- Studying micro‑features on polished sections, etched surfaces, or fracture faces.
- Capturing images for reports, publications, and teaching material.
Evaluate micro‑mechanical parts, sensors, and precision assemblies where both fine detail and overall geometry matter.
- Inspecting gears, springs, and microscale mechanisms in watchmaking, instrumentation, or robotics.
- Checking alignment, clearances, and engagement of moving components.
- Supporting assembly and rework tasks under ergonomic stereo viewing.
Use the microscopes for sample preparation, sorting, and observation in routine and advanced life‑science workflows.
- Handling and dissecting biological samples with a large, bright stereoscopic field of view.
- Screening model organisms, tissues, or cell cultures at low to medium magnifications.
- Documenting experiments with calibrated images for lab notebooks and reports.
Robust optics and encoded reproducibility make the systems well suited for training labs, shared facilities, and routine inspection stations.
- Teaching correct inspection techniques using shared stereo views and digital images.
- Standardizing setups so students and operators obtain comparable results.
- Using documented examples as references for future evaluations.
Frequently Asked Questions
No. Core viewing and stereoscopic operation are available without a PC. Motorized functions on the M205 A can be controlled via external devices such as SmartTouch, hand wheels, or a footswitch, and software can be added for advanced documentation and analysis.
Typical applications include medical device manufacturing, semiconductor and electronics inspection, and materials science, as well as general industrial inspection and research tasks that require high‑quality stereo imaging.
Encoded zoom continuously sends magnification and diaphragm settings to the software so that scale bars and calibration update automatically and are stored with each image, making results easy to repeat and compare.
FusionOptics combines one optical path optimized for maximum resolution with another optimized for depth of field. Your brain merges the information from both paths into a single 3D image with outstanding detail and depth.
The M125 C provides a 12.5:1 zoom with typical total magnification of about 8×–100×, while the M205 C and M205 A offer a 20.5:1 zoom with roughly 7.8×–160×, depending on the chosen objective and eyepieces.
The M205 A is fully motorized, allowing automated control of zoom, focus, and illumination for repetitive, high‑precision workflows. The M125 C and M205 C are encoded but use manual zoom and focus.
These microscopes are typically used with Leica Application Suite or LAS X software for image acquisition, measurements, autofocus, tile scanning, and report generation.
Yes. Various adapters and C‑mount video tubes are available so that you can connect compatible Leica or third‑party cameras for documentation and analysis.
The encoded M125 C, M165 C, M205 C, and M205 A can be combined with motor focus columns and compatible scanning stages, enabling automated Z‑stacks and tile scans with appropriate software.
A wide range of incident and transmitted LED illumination options is available, including near‑vertical illuminators and specialized transmitted‑light bases, so you can optimize contrast for different sample types.


